ASD-Notes
My notes on Advanced-Software-Development
Architecture & Patterns
- Architecture Centred Approach
- Introducing Patterns
- Key Architecture Patterns
- Layered Architecture
- Advice: Multi-Tier Layered Architectures
- Layered Architecture
- Simple Logical Architecture
- Advice: An Application Coordination Layer
- Model-View Separation Principle
- More Benefits of Layered Architecture
- Reference Architectures
- OSI Model for Distributed Systems
- Internet Stack (TCP/IP Model)
- Layering Considered Harmful (?)
- Basic Web 2.0 Reference Architecture Diagram
- Patterns and Concurrency
- Conclusion
- Resources
Architecture Centred Approach
- We place an emphasis on design
- Design pervades engineering activities
- Important aspect of Computer Science
- An incorrect interpretation of the Agile Development leads to inadequate levels of architectural design information
- Architecture Decisions are system-wide Strategic Decisions
- Choice of programming paradigm, e.g.: Object-orientation
- Choose overall architectural pattern
- Choice of API(S)
- Local detailed tactical decision e.g.: algorithms are left for later
Requirements and Analysis leads to design
- At first we are investigators learning about a problem
- Then we change roles and become designers producing a working solution
- (and then we change back iteratively!)
What is Software Architecture Then
- Software architecture -> large scale
- big ideas
- motivations
- constraints
- organisation
- patterns
- responsibilities
- connections
- Very interested in the non-functional requirements
- also called quality requirements
- e.g.: security, persistence, usability, etc
- ensure that these can be met
- or if cannot be met, suggest trade-offs
- e.g.: trends vs costs vs time vs usability vs security
Architecture is the Important Stuff
- Expert developers understanding of the system design
- The set of design decisions that must be made early on
- e.g.: trends vs costs vs time vs usability vs security
- also called quality requirements
- Decisions that are hard to change
- The important stuff
- Whatever that is
Introducing Patterns
- Whatever that is
- big ideas
- Think about your own programming style
- A large portion of it is most likely the way you structure your solutions, rather than the minute details of your code
- If you could reuse the structure from one project to the next, you would gain all the benefits of reuse
- IT designer community has a growing body of past computer solutions for ideas and inspiration
- Best described using patterns
Patterns are Encapsulated Experience
- Software design does not begin with an empty slate
- A new design is based on experience of previous ‘similar’ designs
- Software Design Patterns (SDP) attempt to guide new design with insight into typical problems
- They attempt to encapsulate the basic approaches for similar types of problems
Patterns applied to Software Development
- The idea of named patterns for software originated with Kent Beck (eXtreme Programming guy) in the mid 1980s
- Software patterns really popularized with book:
- Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software by Gamma, Helm, Johnson, and Vlissides
- Frequently referred to as the Gang of Four (GoF)
Original Idea is from (real) Architecture
- Frequently referred to as the Gang of Four (GoF)
- Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software by Gamma, Helm, Johnson, and Vlissides
- Christopher Alexander, an architect, captured solutions to recurring problems
- These problems and solutions were described as patterns
Each pattern describes a problem that occurs over and over again in our environment and then describes the core of the solution to that problem in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over without ever doing it the same way twice Each pattern is a three-part rule, which expresses a relation between a certain context, a problem and a solution
- These problems and solutions were described as patterns
- Definition a pattern is a solution to a problem in a context
Real v Software Architecture
- Software is not embedded in space
- Often no constraining physical laws
- Software is (infinitely) malleable
- Software has no obvious representation
- E.g.: no familiar geometric shapes
- Software does stuff - it is active
Aims of Software Patterns
- The aim is to enhance reusability of object-oriented code
- Well-structured object-oriented systems have recurring patterns of classes and objects
- Knowledge of the patterns that have worked in the past allows
- A designer to be more productive
- The resulting designs to be more flexible and reusable
Benefits of All Design Patterns
- Capture expertise and make it accessible to non-experts in an encapsulated design pattern
- Help communication amongst developers by providing a common language
- Improve design understandably
- Make it easier to reuse successful designs and void alternatives that diminish reusability
- Facilitate design modifications
- The design is more easily understood
- Improve design documentation
- The system documentation starts with the UML design pattern
Definition: Architectural Patterns
An architectural pattern is a set of architectural design decisions that are applicable to a recurring design problem, and parameterized to account for different software development contexts in which that problem appears.
- The system documentation starts with the UML design pattern
- Architecture Model
- An artefact documenting some or all of the architectural design decisions about a system
- Architecture Visualization
- A way of depicting some or all of the architectural design decisions about a system to a stakeholder
- Architecture View
- A subset of related architectural design decisions
Key Architecture Patterns
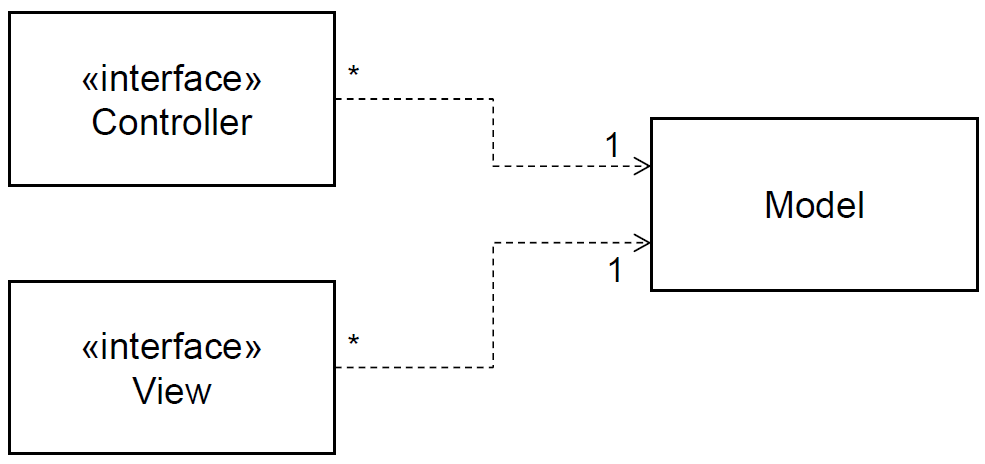
Model-View-Controller (MVC) Pattern
| | Description | |—|—| |Problem|Used when there are multiple ways to view and interact with data. Also used when the future requirements for interaction and presentation of data are unknown | |Solution|Separates presentation and interaction from the system data. The system is structure into three logical components that interact with each other. The Model component manages the system data and associated operations on the data. The View component defines and manages how the data is presented to the user. The Controller component manages user interactions (e.g.: key presses, mouse clicks, etc) and passes these interactions to the View and the Model| |Pro|Allows the data to change independently of its representation and vice versa. Supports presentation of the same data in different ways with changes mode in on representation shown in all of them | |Con| Can involve additional code and code complexity when the data model and interactions are simple |
- A subset of related architectural design decisions
Layered Architecture Pattern
| | Description | |—|—| |Problem | Used when building new facilities on top of existing systems; when the development is spread across several teams with each team responsibility for a layer of functionality; when there is a requirement for multi-level security.| |Solution|Organises the system into layers with related functionality associated with each layer. A layer provides services to the layer above it so the lowest-level layers represent core services that are likely to be used throughout the system| |Pro| Allows replacement of entire layers so long as the interface is maintained. Redundant facilities (e.g.: authentication) can be provided in each layer to increase the dependability of the system| |Con|In practice, providing a clean separation between layers is often difficult and a high-level layer may have to interact directly with a lower-level layer rather than through the layer immediately below it. Performance can be a problem because of multiple levels of interpretation of a service request as it is processed at each layer|
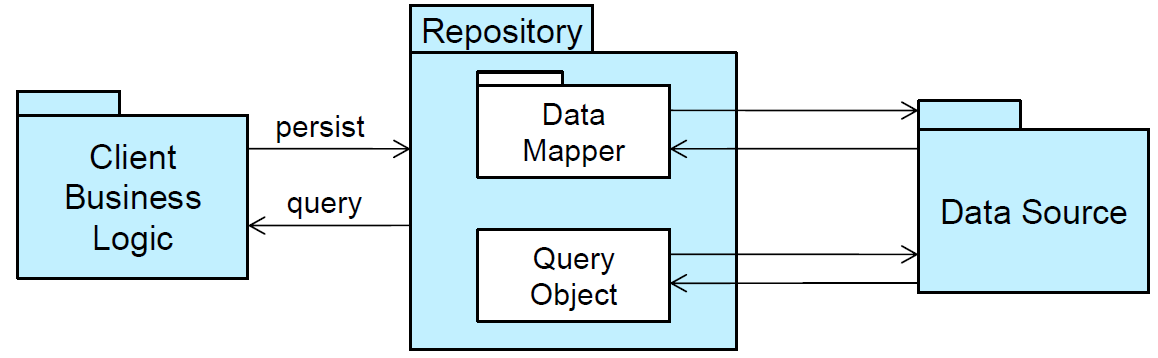
Repository Pattern

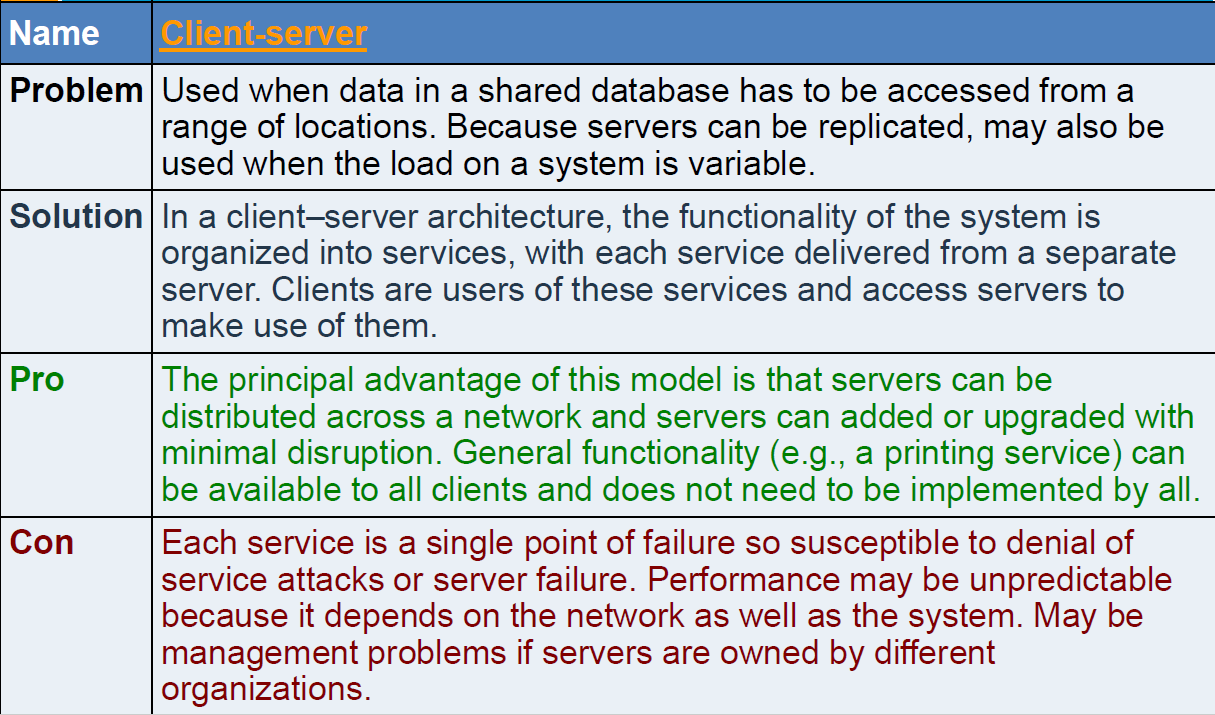
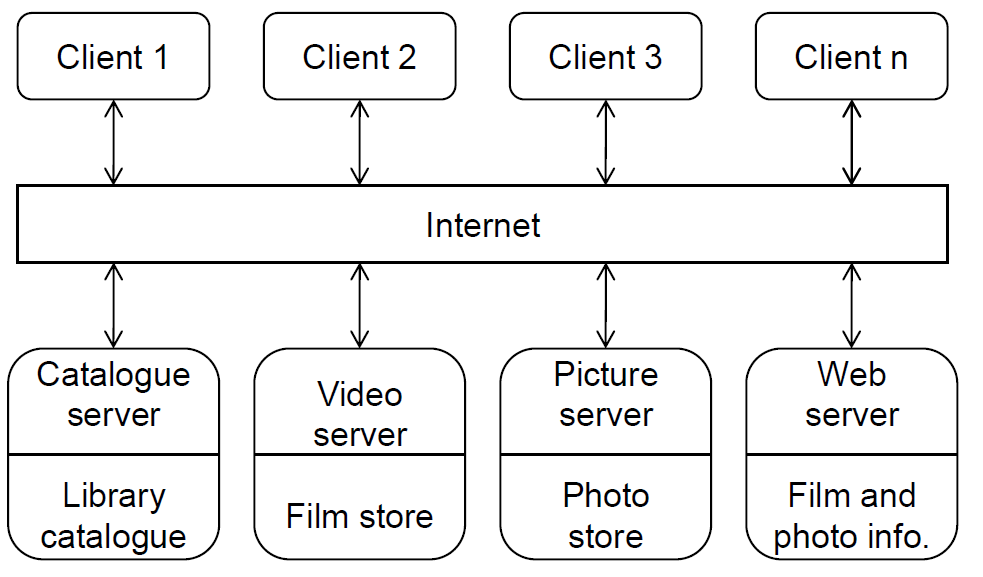
Client-Server Pattern
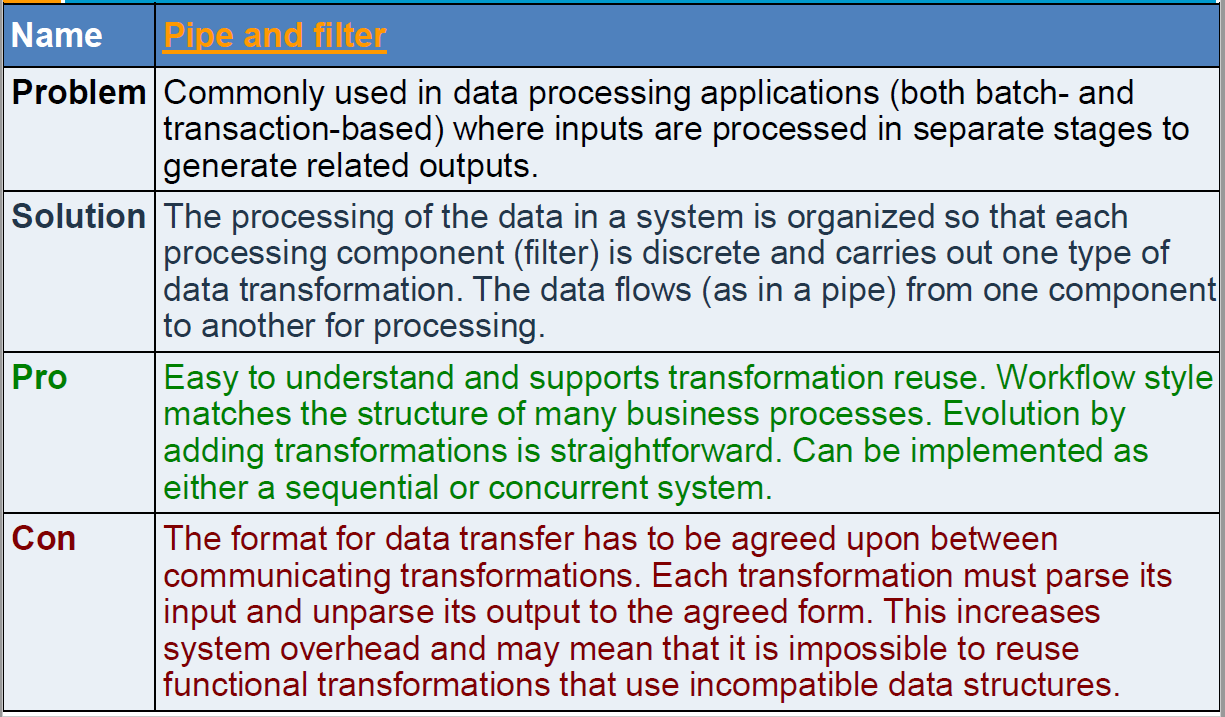
Pipe and Filter Pattern
Key Aim of these Patterns
- Cohesion
- Degree to which communication takes place within the module
- Coupling
- Degree to which communication takes place between the modules
- Minimize coupling while maximising cohesion
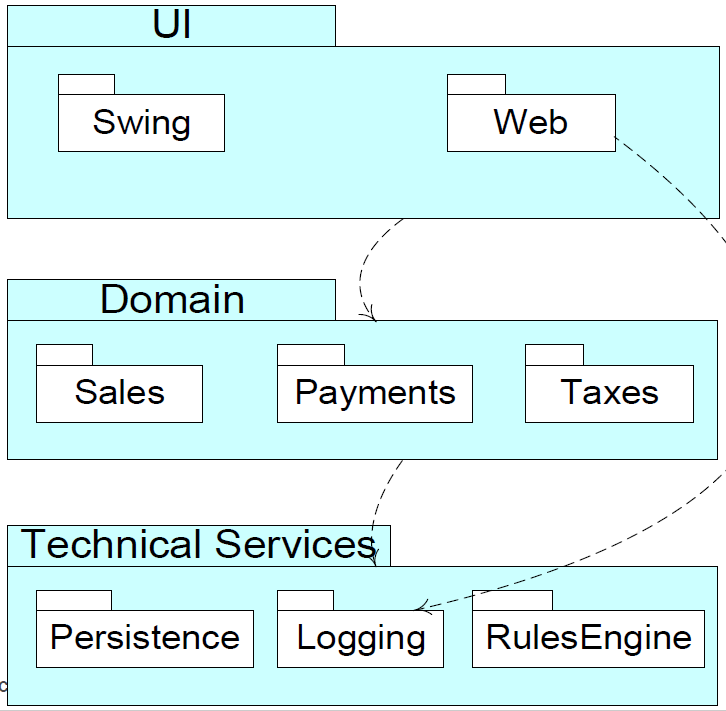
Layered Architecture
Advice: Multi-Tier Layered Architectures
- Separate presentation and application logic, and other areas of concern
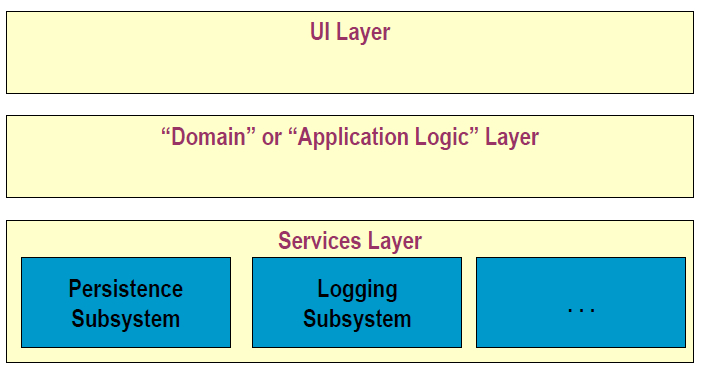
Layered Architecture
- Logical architecture organised into layers
- Layer - very coarse-grained grouping of classes (or packages or subsystems) with cohesive responsibility for a major aspect of the system
- Relationship between layers
- “higher” layers call services of “lower” layers
- Strict Layered Architecture (SLA) - layer uses only layer directory below
- Relaxed - can use several lower layers
- Typical layers in an OO system:
- User interface
- Application Logic and Domain Objects
- Technical Services
- Application-independent, reusable across systems
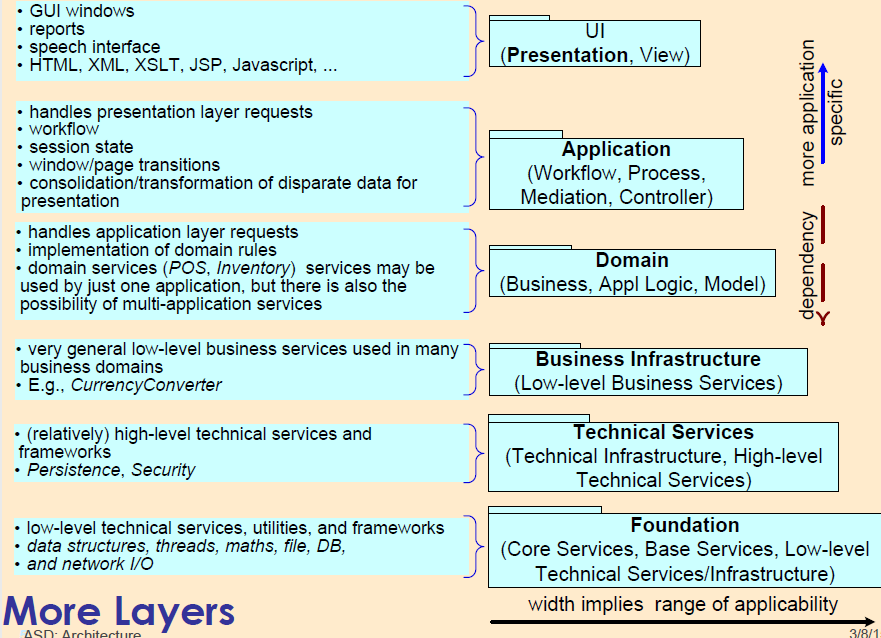
Simple Logical Architecture
- Application-independent, reusable across systems
- In the UML, the logical partitioning is illustrated with package diagrams
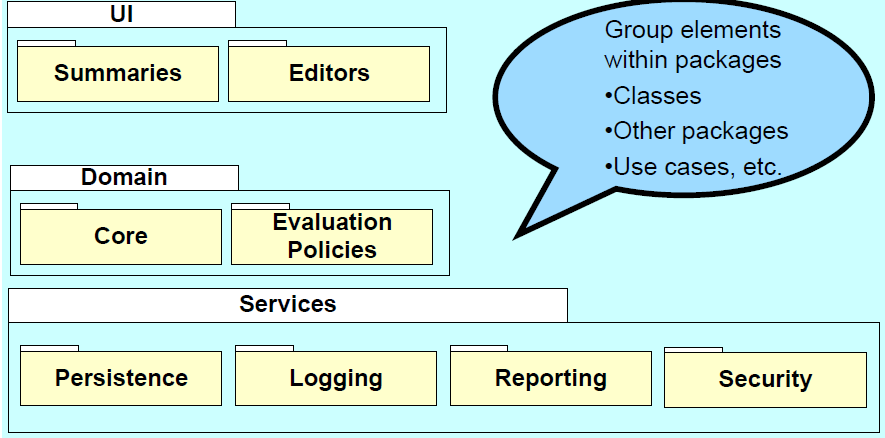
Advice: An Application Coordination Layer
- One strategy is to have “application coordination layer” whose objects represent use cases.
- They may also hold session state
Can mix and match different architectural patterns
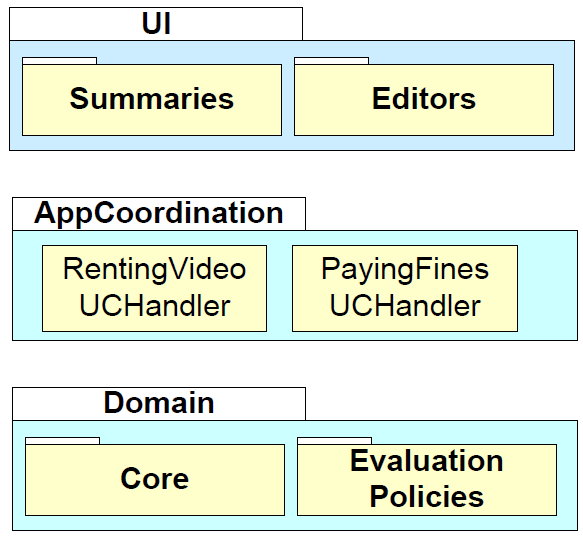
- They may also hold session state
Model-View Separation Principle
- Model == domain layer
- View is the User Interface (UI) layer
- Model objects shouldn’t have knowledge of View objects
- Don’t assign domain responsibility to View objects
- Better separation of concerns with lower coupling
- When domain layer independent of UI layer, domain layer can be used with another UI layer
- Facilitates multiple views of a given model
- Example: Application and web UIs for a given application
More Benefits of Layered Architecture
- Example: Application and web UIs for a given application
- System easier to comprehend: each layer has specific purpose
- Facilitates ‘high-cohesion’ within layers and ‘low-coupling’ between layers
- Prevents source code changes from rippling throughout system
- Code changes should be confined within a specific layer
- Minimizing coupling makes it easier to swap out a technical service in a lower layer and replace it with another technology
- Replacing RDBMS without major code re-write in application logic
- Lower layers contain reusable functionality
Reference Architectures
- Idealized way of discussing and comparing domain-specific architectures
- They do not represent actual real systems
- Reference architecture features make them easier to describe and understand
- A reference model provides a vocabulary for comparison
- It acts as a base against which systems can be evaluated
OSI Model for Distributed Systems
- OSI stack is seven-layer model for open systems interconnection
- Lower layers: physical interconnection,
- Middle layers: data transfer
- Upper layers: semantically meaningful application information
- Allows conformant systems to communicate with each other
- Each layer should depend on the layer below
- Performance problems with this layered approach
- Vast physical differences between networks
- Well defined functional characteristics but not the non-functional
- Developers implement their own higher-level facilities and skip layers in the model
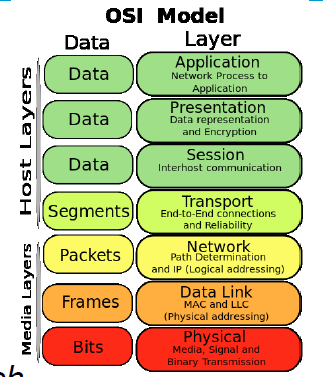
Internet Stack (TCP/IP Model)
- Internet stack is similar layered networking stack to OSI
- Pre-dates OSI stack
Layering Considered Harmful (?)
- Networking layering -> functions of each layer are carried out completely before protocol data unit is passed to the next layer
- Optimization of each layer has to be done separately
- Hides information that lower layers may need to optimize performance
- Layered model (TCP/IP & ISO OSI) causes conflict:
- Layer N may duplicate lower level functionality (hop-hop error recovery vs end-to-end error recovery)
- Layers may need the same information (time stamp)
- Layer N mau need layer N-2 Information (lower layer packet sizes)
- Increased layering -> increased complexity (via inter-layer dependencies)
It is always possible to agglutinate multiple separate problems into a single complex interdependent solution. In most cases this is a bad idea Agglutinate - combine to express compound ideas.
- Conclusion
- Horizontal separation may be more cost-effective and reliable than vertical
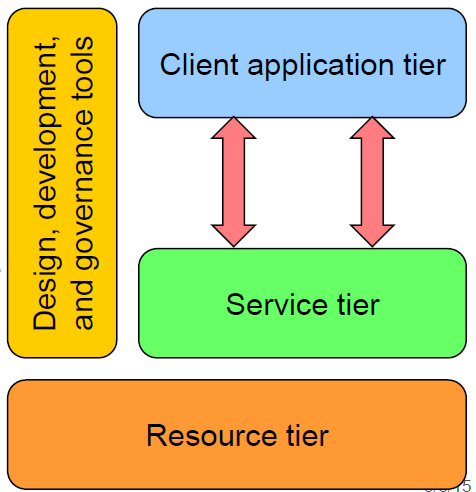
Basic Web 2.0 Reference Architecture Diagram
- Horizontal separation may be more cost-effective and reliable than vertical
- Resource tier
- Capabilities or backend system (data or processing) that support services consumed over the internet
- Service tier
- Packages resources as a service and controls what goes in and out
- Application servers deploying SOAP, EJB, PHP, Rails, ASP
- Connectivity
- Means to reach service
- Standards/protocols like XML over HTTP
- Client tier
- User view of services
- Web browsers, Flash, Acrobat, iTunes
- Design, development and governance tools
- To build web apps
- Adobe Dreamweaver and Apple’s tools (xCode, DashCode), other IDEs
Patterns and Concurrency
Parallel or Concurrent Programming
- The way to go
- Multi-core
- Server farms
- Up to now processing speedup has been due to processor speedup (Moore’s law), but this is coming to an end
- Solution is parallel (or concurrent) processing
- A parallel program is the specification of a set of processes executing simultaneously, and communicating among themselves in order to achieve a common objectives
- This is a very big, tough, increasingly important topic
- Consider a few patterns that can potentially allow parallel execution
Moore’s Law
The complexity for minimum component costs has increased at a rate of roughly a factor of two per year. Certainly over the short term this rate can be expected to continue, if not to increase. Over the longer term, the rate of increase is a bit more uncertain, although there is no reason to believe it will not remain nearly constant for at least 10 years.
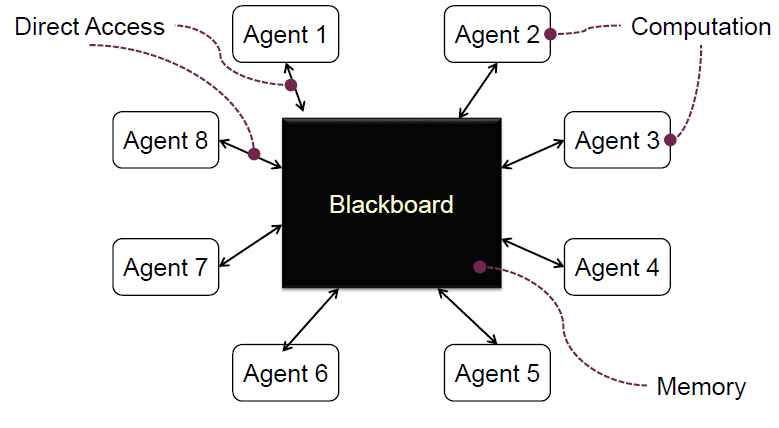
Repository (or Blackboard)
- Suitable for applications in which the central issue is establishing, augmenting, and maintaining a complex central body of information
- Typically the information must be manipulated in a wide variety of ways
- An example of a repository or blackboard architecture may the management of work allocation process in a company
Parallel Agent and Repository
- Data-centred concurrency
- Autonomous agents update state managed in a central repository
- Repository (Blackboard) of the resulting creation that is shared by all agents
- Logical structure may be in a shared memory in a multi-core machine
- Can be distributed among agents as a block it owns
- Agents intelligent agents that wil act on blackboard
- Controller orchestrates agents access to the repository and creation of the aggregate result
- Can reside either in the agents or the blackboard
Client-Server Architecture
- Distributed system model which shows how data and processing is distributed across a range of components.
- Can provide coarse grained parallelism
- Can be implemented on a single computer
- Set of stand-alone servers which provide specific services such as printing, data management, etc
- Set of clients which call on these services
- Network which allows clients to access servers
Client-Single Server
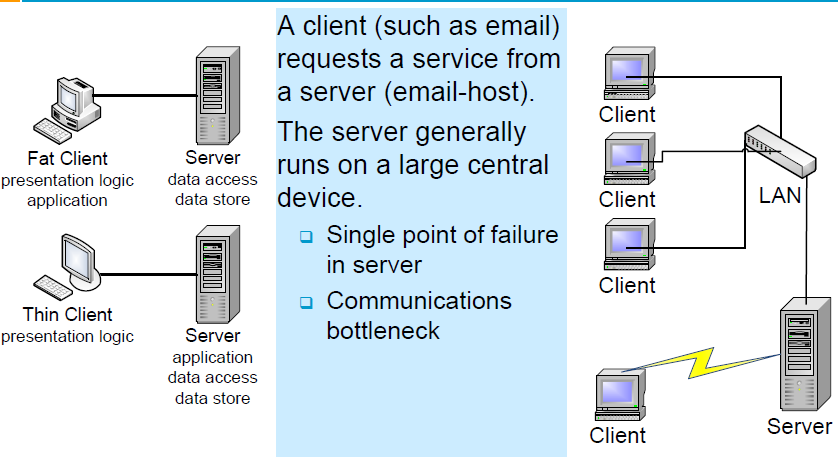
Client-Server and Peer-to-Peer Architecture
- Internet Mediated Client-Server
- Dominant architecture for internet
- Add redundancy (server-farms or cloud)
- Vulnerable to attack (DOS)
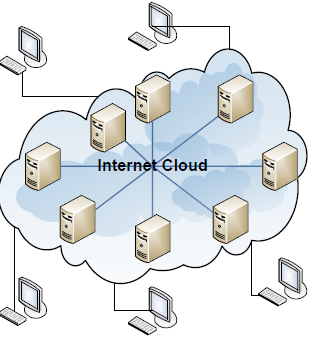
- Two-Tier Peer-2-Peer Architecture
- Many devices perform server-functions
- Any device that that is acting as a client is able to find server (with the assistance of other servers)
Pipeline or Pipe and Filter Pattern
- Suitable for applications that require a defined series of independent computations to be performed on ordered data
- Very useful if each computation can be done incrementally on the data
- Then computations can proceed in parallel
- Very useful if each computation can be done incrementally on the data
- The pattern attempts to decompose the problem into a set of computations, or filters, with operations, called pipes to stream data from one process to another
- The filters interact only via pipes
- “pure” filters have local processing and little state
Pipes and Filters in Parallel
- The components of the pattern execute in parallel
- All filters and pipes are simultaneously active
- they accept the data
- but only filters operate on them
- and send them to the next step
- Pipes synchronize the activity between filters
Although, in parallel the pip and filter will look like this:
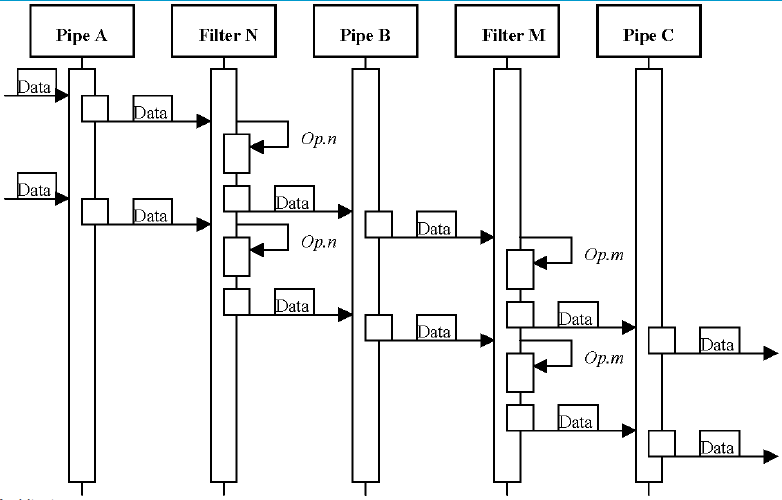
Scenario of Pipes and Filters
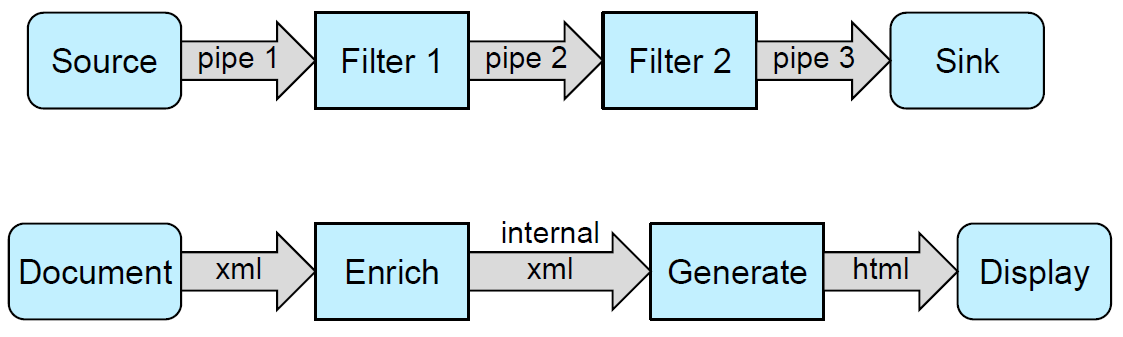
- Pipe A receives data from a Data Source or another previous filter, synchronising and transferring it to the Filter N
- Filter N receives the package of data, performs operation Op.n on it, and delivers the result to Pipe B.
- At the same time, new data arrives to the Pipe A, which delivers it as soon as it can synchronise with Filter N
- Pipe B synchronises and transfers the data to Filter M
- Filter M receives the data, performs Op.m on it, and delivers it to Pipe C, which sends it to the next filter or Data Sink
- Simultaneously, Filter N has received the new data, performed Op.n on it, and syncrhonised with Pipe B to deliver it
- The previous steps are repeated over and over until no further data is perceived from the initial Data Source or previous filter
Conclusion
Realizing Non-functional Requirements
Performance
- Localize critical operations and minimize communications
- Use large rather than fine-grained components. Allow for concurrency
Security
- Use a layered architecture with critical assets in the inner layers
Safety
- Localize safety-critical features in a small number of sub-systems
Availability
- Include redundant components and mechanisms for fault tolerance
- Allow replacement of components without stopping the system
Maintainability
- Use fine-grained, replaceable components
- Avoid global/shared data structures
Architecture Diagrams
- Simple Block Diagrams
- Simple, informal block diagrams showing entities and relationships
- Most frequently used method
- Good for communicating at a higher level of abstraction
- Diagrams with Rich Semantics
- Do not show the types of relationships between entities
- Do not show visible properties of entities (interfaces)
- Costly ot produce, time consuming
Purpose of Architecture: beforehand
- Software architecture can serve as a design plan for the negotiation of system requirements
- A means of structuring discussions with clients, developers and managers
- An essential tool for complexity management, hiding details, allowing the designers to focus on the kyy system abstractions
Use of Architectural Models after Development
- A way of documenting an architecture that has been designed
- To produce a complete system model showing the system components, their interfaces and their connections
- For later maintenance and enhancements
- For other developers needing to integrate with your systems
Resources
Sommerville:
- Chapter 6 Architectural Design <- important
- Chapter 13 Dependability Engineering
- Chapter 20 Embedded Systems
- Chapter 28 Application Architectures -> Here
Bennet, McRobb & Farmer
- Chapter 13 System Design and Architecture
-
Chapter 15 Design Patterns
- Partha Kuchana, Software Architecture Design Patterns in Java
- Monroe, R.T., Kompanek, A., Melton, R., Garlan, D., Architectural styles, design patterns and objects -> Here
- Mary Shaw. 1996. Some patterns for software architectures. In Pattern Languages od Program design 2. -> Here