ASD-Notes
My notes on Advanced-Software-Development
Agile Development
- Introduction
- What is Agile Software Development?
- Principles of Agile Methods
- Teams Must Be Empowered
- Agile Manifesto
- Pareto’s Law - 80/20 Rule
- Fixed Timescale
- Bare Requirements
- Agile Development Cycle
- Extreme Programming
- Testing
- Refactoring
- Conclusion
- Collaboration with Users
- Agile method applicability
- Problems with agile methods
- Agile methods and software maintenance
- Plan-driven specification and development
- Agile specification and development
- Architecture Change and Refactoring
- Summary - Points to consider
- Remember Principles of Agile Methods
- Active User Involvement
- Remember Fixed Timescale
- Remember That Agile Requirements are Barely Sufficient
- ADT - The Cycle
- Frequent Delivery
- Regular Release Cycle
- eXtreme Programming (XP)
- TDD
Introduction
Agile is a set of values and principles. Agile Manifesto
What is Agile Software Development?
- Put the software being developed first
- Acknowledge that user requirements change
- It is agile because it can respond quickly to the users changing needs
- Advocates frequent and regular, software released
- Users can respond quickly to these releases, changing requirements
Thats not what we meant!
Principles of Agile Methods
| Principle | Description | | — | — | | Customer Involvement | Customers should be closely involved throughout the development process. Their role is to provide and prioritize new system requirements and to evaluate the iterations of the system | | Incremental Delivery | The software is developed in increments with the customer specifying the requirements to be included in each increment. | | People not process | The skills of the development team should be recognized and exploited. Team members should be left to develop their own ways of working without prescriptive processes. | | Embrace Change | Expect the system requirements to change and so design the system to accommodate these changes | | Maintain Simplicity | Focus on simplicity in both the software being developed and in the development process. Wherever possible, actively work to eliminate complexity from the system. |
Teams Must Be Empowered
- Users can respond quickly to these releases, changing requirements
- The project team must have sole responsibility to deliver the product
- Any interference with the project team is disruptive and reduces their motivation to deliver
- The team must together
- Establish and clarify the requirements
- Prioritise them together
- Agree to the tasks required to deliver them
- Estimate the effort involved
- It ensures the buy-in and commitment from the entire project team from the outset
- When challenges arise, the team feels a real sense of ownership
Agile Manifesto
We are uncovering better ways of developing software by doing it and helping others do it. Through this work we have come to value:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
That is, while there is value in the items on the right, we value the items on the left more.
If you can dodge a wrench you can dodge a requirement
Pareto’s Law - 80/20 Rule
- Typically 80% of your results may actually come from only 20% of your efforts!
- Try to apply the 80/20 rule, and focus on the important 20% of effort that gets the majority of the results
- The difficult question is can you see initially which 20% is the important 20%?
- The 20% that will deliver 80% of the results
- In very many cases, the answer is NO
Fixed Timescale
Time Waits for No-one
- In Agile Development, requirements evolve, but timescales are fixed
- Contrast to traditional development
- Capture all known requirements
- Changes are subject to change control
- Users are told it’s much more expensive to change or add requirements during or after the software is built
- It becomes imperative to include everything they can think of, everything they ever dreamed of
- Normally
- Users may actually use only 20% or less of the product
- Many projects start with a bloated scope
- No-one is sure at the outset which 20% they will use
- It is impossible to think of everything, things change, and things are understood differently
- Agile development assumes that requirements emerge and evolve
- However much analysis and design you do, you cannot really know what you want until you see and use the software
- In the time spent analysing and reviewing requirements and designing a solution, external conditions could change
Fixed Budget
- What does business expect from development teams?
- Deliver and agreed business requirements
- On time and within budget
- To an acceptable quality
- In agile development, it is the scope that is variable, not the cost and timescale
- For this to work, it’s imperative to start development with the core, highest priority features
- Delivered in the earliest iterations
- As a result
- Business has a fixed budget
- Based on affordable resources
- Thus, can make plans based on a certain launch date
Bare Requirements
Agile Requirements are Barely Sufficient
- Capture requirements at a high level and on a piecemeal basis
- Just in time for reach feature to be developed
- Barely sufficient
- The minimum to enable development and testing
- Minimise the time spent on anything not part of product
- The minimum to enable development and testing
- Understand enough to determine the scope and for high level budgetary estimates
- Captured in collaborative workshops so that all team members understand the requirements
- Allows everyone to contribute, challenge and understand what’s needed and why
User Stories
- Allows everyone to contribute, challenge and understand what’s needed and why
- Most agile teams represent each requirement as a user story
- Similar to Use Cases but lightweight and simpler
- A simple statement about what a user wants to do with a feature
- Should focus on the who, what and why of a feature, not how
- on a job site, two high-level User Stories might be:
- As a job seeker, I want to search for a job, so I can advance my career
- As a recruiter, I want to post a job vacancy, so I can find a new team member
- on a job site, two high-level User Stories might be:
- The general form can be
- As a [user role], I want to [goal], so I can [reason]
- At the start of a project, capture an initial list of User Stories up-front
- Useful for estimating and planning
- Defer capturing the details until the story is prioritised and due to be developed
- Users often tell stories
- About the failings of their current system
- How they see things working better in future
- Capture these stories as User Stories, as they are told
- In traditional development projects, these stories are captured in a lengthy analysis process and available in a lengthy document
- Not user friendly
Recording User Stories
- Not user friendly
- Written on postcard size cards in 3 parts
- Heading
- Name/description of the user story, reference numbers, estimated size, etc
- Conversation (on the front of the card)
- Information about the user story + what system is meant to do
- A sketch or diagram of the feature
- Notes about how it should function
- Information about the user story + what system is meant to do
- Confirmation (on the back of the card)
- Test cases to help identify scenarios that users, developer and/or analysts may not have thought of
- Heading
- Writing User Stories on a card ensures requirements are broken into small manageable pieces of functionality
- Cards can be supported by documentation, but keep it to the bare minimum to allow a feature to be developed, and always in very small units.
- Requirements should be broken into tasks of no more than 16 hours or preferably 8 hours, so progress can be measured daily
- All items are deliverables not activities or tasks
- You can see a deliverable to judge it in quality and completeness
- A task you cannot
Incremental Design
- As opposed to Fred Brooks No Silver Bullet Agile does not follow a top-down design method
- Top-down design says: time in design is worth it to save cost of re-working the design many times
- Agile design is always the same size as the system
- “You can’t possibly anticipate the problems and alternatives that will arise once you start coding”
- If a new feature comes along that requires major changes then that is the trade-off for the flexibility it allows
- Perhaps this feature was not even known at the beginning anyway!
- Or it might have gone away if we knew of it at the start!
Agile Development Cycle
- The cycle is Analyse, Develop, Test; Analyse Develop, Test
- Doing each step for each feature, one feature at a time
ADT
- Doing each step for each feature, one feature at a time
- Advantages of this approach include;
- Reduced risk
- Increased value: delivering some benefits early
- More flexibility/agility
- Better cost management
- Each feature must be fully developed, to the extent it can be shipped
- Develop features in priority order
How Frequent is Frequent enough?
- Competitors won’t wait
- Speed-to-market - a significant competitive edge
- The value of first-mover advantage is enormous
- Research shows 80% of first to market end up market leaders
- There is no right or wrong answer
- Decide what’s appropriate; stick to a regular release cycle
- Allows you to plan
- Allows your infrastructure and ops team to plan
- Allows your business colleagues to plan
- Allows launch events, marketing campaigns, etc to be planned
- Decide what’s appropriate; stick to a regular release cycle
- BUT - Frequent releases of buggy software can really irritate customers
Done Means Done
- Features developed in an iteration, should be 100% complete by the end of the iteration
- Ideally, each iteration results in a release
- In Agile development, Done! means shippable
- In practice a feature may rely on other features being completed before the product could really be shipped
- But the feature on its own merits should be shippable
- In practice a feature may rely on other features being completed before the product could really be shipped
- Completing each feature before moving onto the next ensures the system is not in a state where multiple features are 90% complete or untested, as in traditional developments
Working Product at All Times
- Meaning 1
- A software product should always be in a working state
- Not always functionally complete, just that it works and has high quality
- A software product should always be in a working state
- Meaning 2
- The emphasis is on producing a working product and shipping it
- Not on producing documentation that might lead to a product
- The best way to get user feedback is to give a product even if it is only work in progress
- Prototypes are better than a document
- Effort spent getting the product back to a working state is a missed opportunity to be doing valuable work
Prototypes
- Prototype solutions to risky problems helps to increase the chance of having a working product
- Prototypes: an inexpensive way to try out ideas so that as many issues as possible are understood before the real implementation
- Two main classes of prototypes
- The true prototype
- Test implementation to understand a problem before it is implemented for real
- “Tracer bullets”
- Prototype that is intended to gradually turn into the final solution
- The true prototype
Continuous Integration
- An important discipline is to continuously integrate changes
- Frequent integration helps to ensure tha modules will fit together
- Also that the product continues to work with all the changes
- Developer have the bad habit of checking out a number of files and not checking them in again until their work is done
- Developers should integrate their work daily
- This gradual introduction of changes ensures that integration problems or regressions are caught early
Nightly Builds
- Software should be completely rebuilt from scratch daily
- The result of the build will be an installable product image
- The build should include as many automated tests as possible to catch integration problems early
- If the build or tests fail, fix the problems first thing
- Don’t let anyone integrate any additional work until after the build succeeds again
- There is a risk of multiple bad changes accumulating that will jeopardize the quality of the product Performance
- Don’t neglect performance!
- Performance is a topic that generates passionate discussions in software development
- Some people feel that code clarity is more important and that you should get the code clarity right first and then optimize the 1% to 3% of code that needs it
- Others feel that you should code for performance first, because if you don’t, your code will always be slow
Extreme Programming
Principles
| Principle | Description| | — | — | | Incremental planning | Requirements are recorded on story cards and the stories to be included in a release are determined by the time available and their relative priority. The developers break these stories into development ‘Tasks’. | | Small releases | The minimal useful set of functionality that provides business value is developed first. Releases of the system are frequent and incrementally add functionality to the first release. | | Simple Design | Enough design is carried out to meet the current requirements and no more. | | Test-First Development | An automated unit test framework is used to write tests for a new piece of functionality before that functionality itself is implemented | | Refactoring | All developers are expected to refactor the code continuously as soon as possible code improvements are found. This keeps the code simple and maintainable | | Pair programming | Developers work in pairs, checking each other’s work and providing the support to always do a good job. | | | Collective ownership | The pairs of developers work on all areas of the system, so no islands of expertise develop and all the developers take responsibility for all of the code: anyone can change anything. | | Continuous integration | As soon as the work on a task is complete, it is integrated into the whole system. After any such integration, all the unit tests in the system must pass. | | Sustainable pace | Large amounts of overtime are not acceptable as the net effect is often to reduce code quality & medium term productivity | | On-site customer | A representative of the end-user of the system (the customer) should be available full time for the use of the XP team. In an extreme programming process, the customer is a member of the development team and is responsible for bringing system requirements to the team for implementation |
System Metaphor in Extreme Programming
- System metaphor is a mental model that everyone shares about the system and it shapes the architecture of the system
- Frequently misunderstood and neglected part of XP
- Difficult to find such a metaphor
- Metaphor is something you start using when your mother asks what you are working on and you try to explain her the details
- Use your common sense or find the person on your team who is good at explaining technical things to customers in a way that is easy to understand
XP Planning Game
Stages
- Release Planning: Requirements for long-term release (months)
- Customers and Developers
- Iteration Planning: Next increment (1-4 weeks work for the team)
- Only developers
| Phases of | Release Planning | Iteration Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Exploration | Customer provides high-value requirements written as user stories | Requirement translated into different tasks recorded on task cards |
| Commitment | Developers commit to the functionality and date for next release | Task assigned to programmers and time to complete estimated |
| Steering | Plan can be adjusted, New requirements added, Existing requirements changed or removed | Tasks are performed and the result is matched with the user story |
Release Planning
- Customer or user is part of XP team and is responsible for making decisions on requirements
- User requirements are expressed as scenarios or user stories
- Team read and discuss the stories, and rank them in order of
- Value to customer
- Risk
- Amount of time they think it will take to implement the story; measured as velocity
- Choose scope: customer selects stories with the features to be implemented in the next release based on these estimates
Iteration Planning
- Stories to be implemented in an iteration are chosen
- Development team break them down into implementation tasks
- Written on task cards
- These tasks are the basis of schedule estimates
- Programmers then accept tasks and the load is balanced between the team members
Iteration Steering
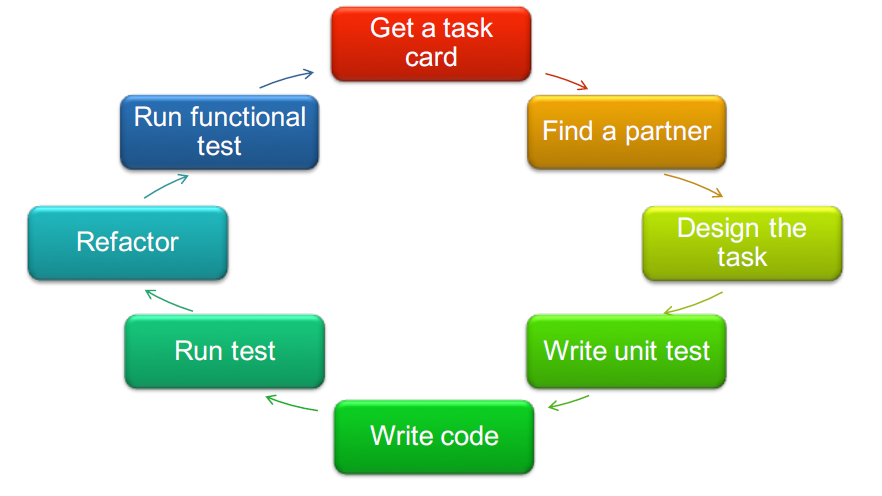
Pair programming in XP
- Programmers work in pairs, sit together to write every line of code
- 2 programmers + 1 Computer = atomic unit of XP code development
- One person at the keyboard, other supporting
- Pairs are created dynamically
- Ego-less development
- Informal review process: each line of code is looked at by at least two people
- Productivity is similar to that of two people working independently
- Common ownership of code
- Individuals are not help responsible for problems with the code
- Collective responsibility for the system
- Team has collective responsibility for resolving problems
- Spreads knowledge across the team
- Reduces risk if someone leaves
- Motivates refactoring as the whole team will benefit from it
Testing
Testing in Agile Development
- Testing in Agile Development
- Testing the software continuously throughout development
- Agile development does not have a separate test phase
- Developers write automated repeatable unit tests
- Testing done as part of the build
- Ensures all features are working each time as build is produced
- Builds should be regular, at least daily
- Integration is done as you go too
- These actions keep the software in a releasible condition throughout the development
- Can be shipped whenever appropriate
Testing in XP
- Can be shipped whenever appropriate
- The XP agile methodology recommends test driven development
- Writing tests before writing code
- Testing can still be done by professional testers
- In agile development testing is more quality assurance than purely testing
- Testing is central to XP and XP has developed an approach where the program is tested after every change has been made
- XP testing features:
- Test-first development
- Incremental test development from scenarios
- User involvement in test development and validation
- Automated test harnesses are used to run all component test each time that a new release is built
Test-first development
- Writing tests before code clarifies the requirements to be implemented
- Tests are programs rather than data
- Executed automatically
- Usually with a testing framework such as junit
- All previous and new tests are run automatically when new functionality is added, thus checking that the new functionality has not introduced errors
Customer Involvement
- Role of the customer in testing is to help develop acceptance tests for the stories implemented in the next release of the system
- All new code is therefore validated to ensure that it is what the customer needs
- Customers have limited time available
- Cannot work full-time with the development team
- May feel that providing requirements was enough of a contribution
- May be reluctant to get involved in the testing process
XP Testing Difficulties
- Programmers prefer programming to testing
- Sometimes they take shortcuts when writing tests
- For example, they may write incomplete tests that do not check for all possible exceptions that may occur
- Sometimes they take shortcuts when writing tests
- Some tests can be very difficult to write incrementally
- In a complex user interface, it is often difficult to write unit tests for the code that implements the ‘display logic’ and workflow between screens
- It is difficult to judge the completeness of a set of tests
- You may have a lot of system tests but your test set may not provide complete coverage
- What are XP/Agile Programmers testing for?
- They don’t have a detailed spec to test against, so how can they possibly test it?
- Agile testing therefore calls for more judgement from a tester
- Not just a case of following a test script
- “testathon” - collaborative programmer brainstorm to write software tests
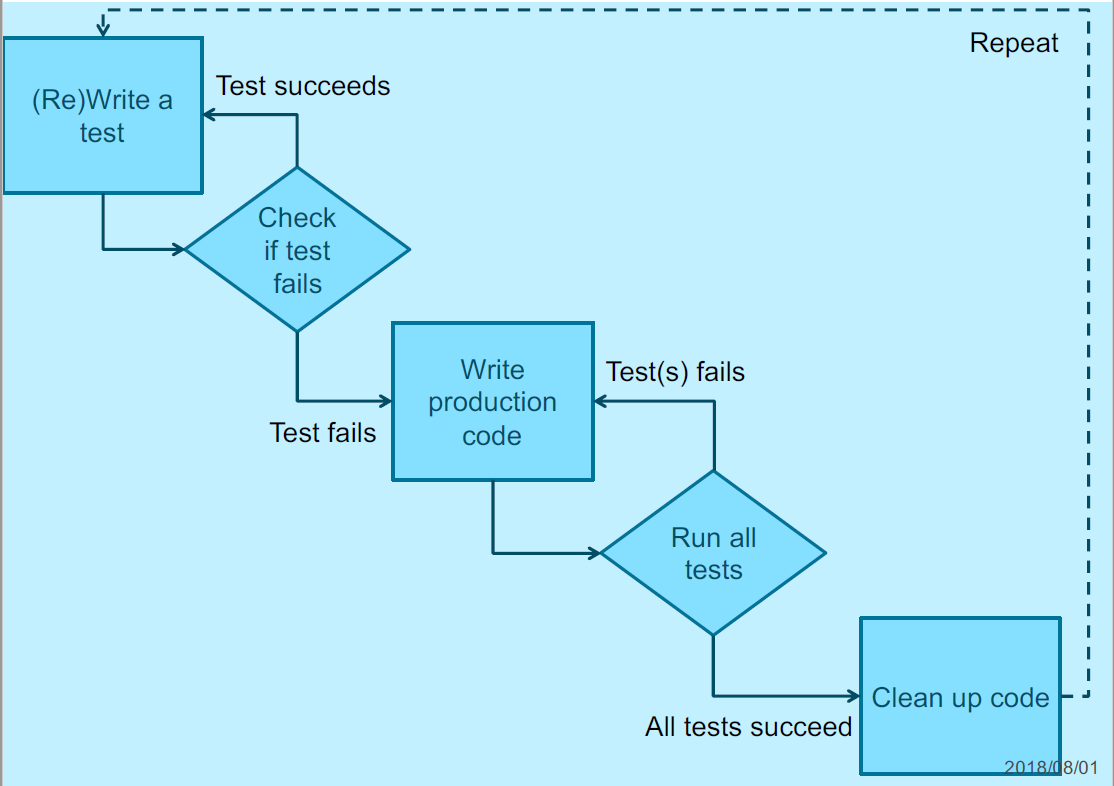
Test First Development
- Quickly add test for new feature
- Just enough code to fail
- Run your tests
- The complete test suite or
- (for speed) a subset, to ensure that new test does in fact fail
- Update the functional code to make it pass the new tests
- Run the tests again
- If they fail update the functional code and retest
- Once the tests pass start over
- Possibly refactoring any duplication duplication out of the design
- Possibly refactoring any duplication duplication out of the design
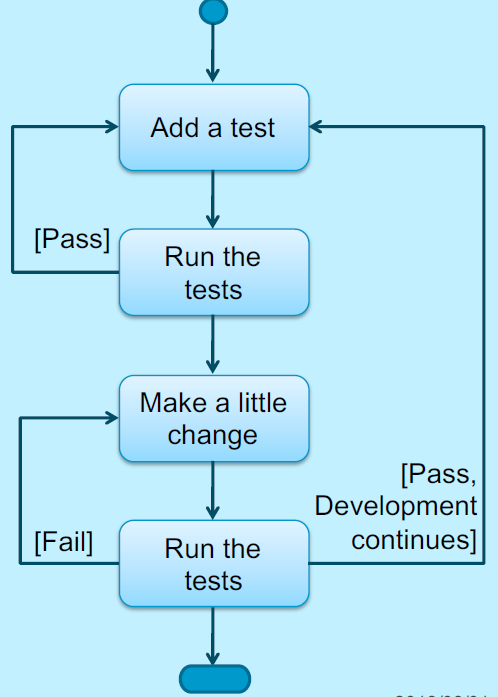
Test Driven Development
- TDD can be described as
- TDD = TFD + Refactoring
- TDD turns traditional development around
- Instead of writing functional code first and then your testing code an afterthought
- You first write your test code before your functional code
- Also you do so in very small steps
- One test and a small bit of code at a time
- With TDD a developer refuses to write a new function unless there is a test that fails because that function isn’t present
- Refuse to add even a single line of code until a test exists for it
- Once the test is in place do the work required to ensure that the test suite now passes
- Once your code works, refactor it to ensure that it remains of high quality
- The diagram show how you perform test driven development:
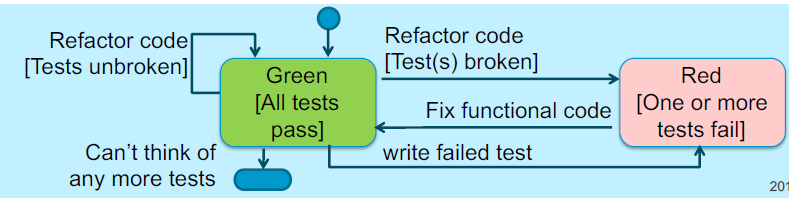
The Rules
- Write new code only when an automated test fails
- Eliminate any duplication
- Generates complex individual and group behaviour. Some technical implications are:
- You design organically, with the running code providing feedback between decisions
- You write your own tests because you can’t wait 20 times per day for someone else to write a test
- Your development environment must provide rapid responses to small changes
- Your designs must consist of highly cohesive, loosely coupled components
- This makes evolution and maintenance of the system easier
Unit Tests
- This makes evolution and maintenance of the system easier
- Implication: developers need to learn how to write effective unit tests
- Experience is that good unit tests
- Run fast
- Have short setups, run times and break downs
- Run in isolation
- You should be able to reorder them
- Use data to make them easy to read and understand
- Use real data when they need to
- Copied of production data
- Represent one step towards your overall goal
- Run fast
- Most programmers don’t read the written documentation for a system
- Instead they prefer to work with the code
- When trying to understand a class or operation most programmers will look for sample code that invokes it
- Unit tests provide a working specification of the functional code
- Unit tests become a significant portion of the technical documentation
TDD Conclusion
- Test-driven development is a development technique where ou must first write a test that fails before you write new functional code
Refactoring
XP and Change
- Conventional wisdom in software engineering is to design for change. It is worth spending time and effort anticipating changes as this reduces costs later in the life cycle.
- XP, however, maintains that this is not worthwhile as changes cannot be reliably anticipated
- Rather, it proposes constant code improvement (refactoring) to make changes easier when they have to be implemented
What is refactoring
- Refactoring is defined as
- a change made to the internal structure of software to make it easier to understand and cheaper to modify without changing its observable behaviour
- Adding functionality does not change existing code, it only adds new capabilities
- measure progress by adding tests and getting the tests to work
- Refactoring does not add functionality, you only restructure the code
- don’t even add any tests - only restructure code
- These software improvements are made before there is an immediate need for them
Refactoring when Developing Software
- Try to add a new function
- (oops) realize this would be much easier if the code were structured differently
- Refactor for a while
- The code is better structured
- Add the new function
- get the new function working
- it is coded in a way thats awkward to understand
- so refactor
Examples of Refactoring
- get the new function working
- Re-organization of a class hierarchy to remove duplicate code
- Tidying up an renaming attributes and methods to make them easier to understand
- The replacement of inline code with calls to methods that have been included in a program libraries
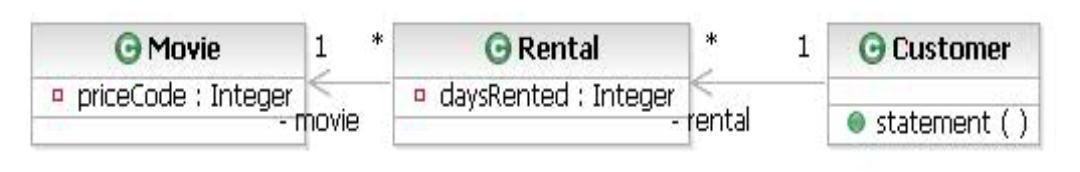
Initial Classes - Video Rental
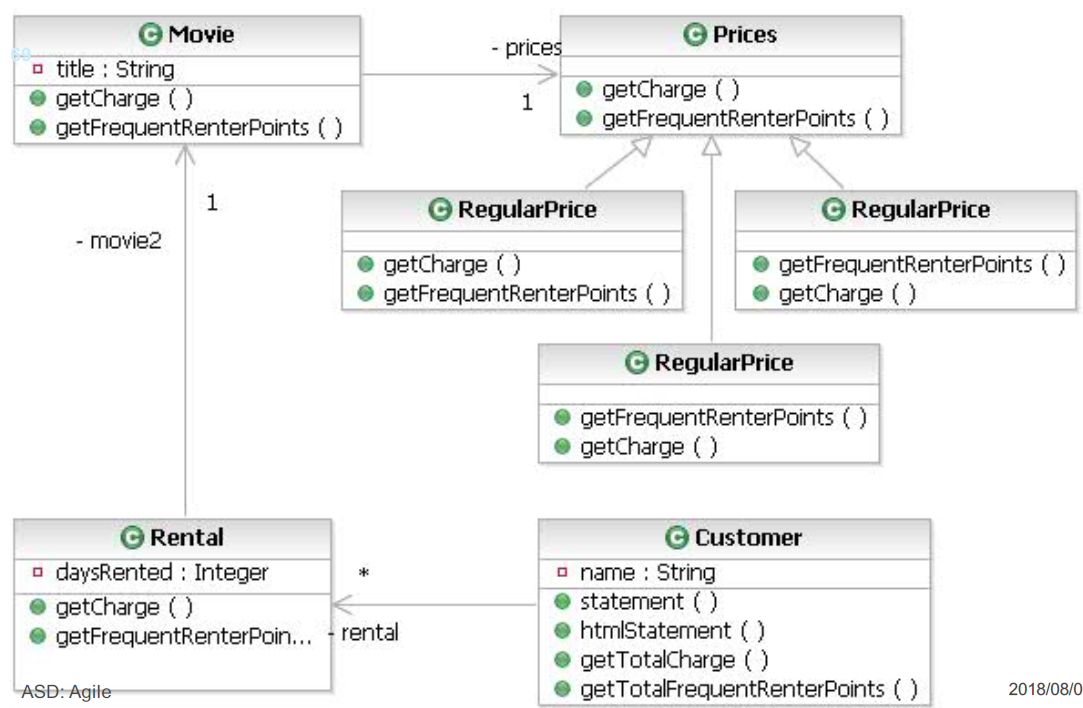
Refactored Classses Video Rental
Why Refactor
Improves the Design of Software
- Deal with Software rot, decay and loss of structure
- Refactoring is like tidying up the code
- Regular refactoring helps code retain its shape
- You refactor code that works but is not ideally structured
- An important aspect of improving design is to eliminate duplicate code
- Ensure the code says everything once and only once
- More code <=> harder to modify correctly <=> more code to understand
- Change this bit of code here, but the system doesn’t do what is expected because you didn’t change that bit over there that does much the same thing in a slightly different context
- Changes are easier to make because the code is well-structured and clear
Makes Software Easier to Understand
- Improve the understandability and readability of the software
- Reduces the need for documentation
- Good programmers write code understandable by human beings
- After code is written it has to be maintained
- Someone will try to read the code and make changes
- It matters if it takes a programmer a week to make a change that would have taken an hour if they had understood your code
- When you are trying to get the program to work, you are not thinking about that future developer
- It takes a change in rhythm to make changes that make code easier to understand
- Refactoring leads to higher levels of understanding that would otherwise be missed during development
Helps find bugs
- By clarifying the structure of the program you clarify certain assumptions you’ve made
- To the point at which even you can’t avoid spotting bugs
- Kent Beck often says about himself:
I’m not a great programmer; I’m just a good programmer with great habits
- Refactoring helps me to be much more effective at writing robust code
Helps you program faster
- Good design is essential for rapid software development
- Changes take longer as you try to understand the system and find the duplicate code
- New feature need more coding as you patch over a patch that patches a patch on the original code base
- Refactoring helps you develop software more rapidly, because it stops the design of the system from decaying
- It can even improve a design
Refactoring Categories
- Composing methods
- The refactorings serve restructurings at the method level
- Moving features between objects
- These refactorings support the moving of methods and fields between classes
- Organizing data
- These refactorings restructure the data organisation
- Simplifying conditional expressions
- These refactorings simplify conditional expressions
- Making method calls simpler
- These refactorings simplify method calls
- Dealing with generalization
- These refactorings help to organise inheritance hierarchies
Refactoring to Patterns
- Refactoring to Patterns is the marriage of refactoring with patterns
- Patterns == classic solution to recurring design problems
- Use patterns to improve an existing design
- Better than using patterns early in a new design
- This is compatible with XP’s desire to avoid too much upfront design
Conclusion
- The traditional view is that refactoring is a waste of resources
Collaboration with Users
- Agile development relies on close cooperation and collaboration between all team members and stakeholders
- Keep requirements and documentation lightweight
- Acknowledge that change is a normal and acceptable reality in software development
- Required to clarify requirements just-in-time
- Keep all team members on the same page throughout the development
- You can’t do away with a big spec up-front and not have close collaboration
Agile method applicability
- Product development where a software company is developing (medium-sized) product for sale
- Custom system development within an organisation, where there is a clear commitment from the customer to become involved in the development process and where there are not a lot of external rules and regulations that affect the software
Problems with agile methods
- It can be different to keep the interest of customers who are involved in the process
- Team members may be unsuited to the intense involvement that characterizes agile methods
- Prioritising changes can be difficult where there are multiple stakeholders
- Maintaining simplicity requires extra work
- Contracts may be a problem as with other approaches to iterative development
- Because of their focus on small, tightly-integrated teams, there are problems in scaling agile methods to large systems
Agile methods and software maintenance
- Most organisations spend more on maintaining existing software than they do on new software development
- So agile methods have to support maintenance as well as original development
- Two key issues
- Are systems that are developed using an agile approach maintainable, given the emphasis in the development process of minimizing formal documentation?
- Can agile methods be used effectively for evolving a system in response to customer change requests?
- Problems may arise if original development team cannot be maintained
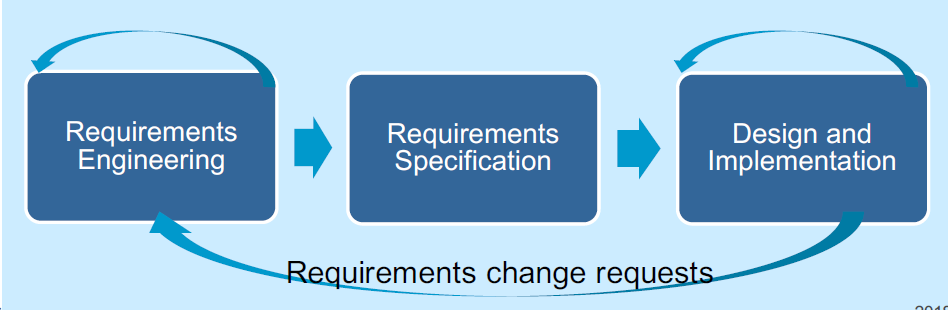
Plan-driven specification and development
- A plan-driven approach to software engineering is based around separate development stages with the outputs to be produced at each of these stages planned in advance
- Not necessarily waterfall model, plan-driven, incremental development is possible
- Iteration occurs within activities
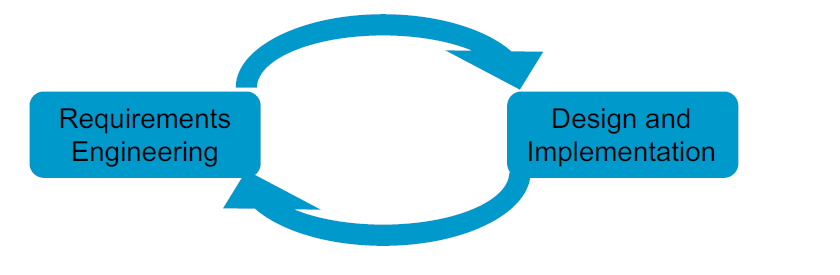
Agile specification and development
- Specification, design, implementation and testing are inter-leaved
- Outputs from the development process are decided through a process of negotiation during the software development process
Architecture Change and Refactoring
- Changes that require architecture refactoring are very expensive
- It is hard to do
- It has consequences for the code and implies code refactoring
Summary - Points to consider
Remember Principles of Agile Methods
- Active user involvement is imperative
- The team must be empowered to make decisions
- Requirements evolve but the timescale is fixed
- Capture requirements at a high level, lightweight and visual
- Develop small, incremental releases and iterate
- Focus on frequent delivery of product
- Complete each feature before moving on to the next
- Apply 80/20 rule
- Testing is integrated throughout the project lifecycle - test early and often
- A collaborative & cooperative approach between all stakeholders is essential
Active User Involvement
- Requirements are clearly communicated and understood at the outset
- Requirements are prioritized appropriately, based on the needs of the user and market
- Requirements can be clarified daily with the project team, not from lengthy documents that are not read or are misunderstood
- Emerging requirements can be factored into the development schedule with the impact and trade-off decisions understood
- The right product is delivered
- As iterations are delivered, check they meet user expectations
- The product is more intuitive and easy to use
- The user is seen to be interested in the development
- The user/business sees the commitment of the team
- Developers are accountable, share progress openly every day
- There is complete transparency as there is nothing to hide
- The user shares responsibility for issues arising; it is not a customer-supplier relationship but a joint team effort
- Timely decisions can be made about features, priorities, issues, and when the product is ready
- Responsibility is shared; the team is responsible together for the delivery of the product
- When the going gets tough, the whole team - business and technical - work together!
Remember Fixed Timescale
- No-one knows what the right solution is at the outset
- Its practically impossible to build the right solution initially
- Traditional project fight change, with change control processes
- Minimise and resist change wherever possible
- Agile development embraces and expects change
- The only thing that is certain in life is change
- Requirements are allowed to evolve, but the timescale is fixed
- To include a new requirement, or to change a requirement, the user must remove a comparable amount of work
- Assumes there are enough non-mandatory features included in the original time frames
Remember That Agile Requirements are Barely Sufficient
- Contrast this to the traditional situation
- User still has new and changed requirements
- Expects the new and existing features to be delivered in the original time frames
- User still has new and changed requirements
- Teams that don’t control changes can end up with scope creep
- One of the most common reasons for projects to fail
- Agile teams accept change and even expect it
ADT - The Cycle
Frequent Delivery
- Agile development is about frequent delivery of products
- Gone are 12 month projects
- a 3-6 month project is strategic
- Consider web
- Products are released early with basic features
- In the web 2.0 its perpetual beta
- derive some benefits early
- get feedback
- look at metrics -> find what works/doesn’t
- before building “everything”
Regular Release Cycle
- Allows you to learn more effectively
- Estimates might be good or bad but they should be consistent
- Estimate features at a granularity of less than 1 day and track your performance
- You’ll begin to understand your delivery rate
- You’ll be surprised at how predictable you can be
- Managing expectations is about predictability
- If people know what to expect, they’re generally happy
- If they don’t they’re not happy
- Focus on frequent delivery of product
- Even more importantly, focus on consistent delivery
eXtreme Programming (XP)
- Whole Team: remove barrier between customer and the rest of the dev team
- Metaphor: Common analogy for the system
- Planning Game: planing specifies the next step
- As the project progresses get a better and better picture of what will be accomplished
- Client expresses goals through user stories - overall behaviour of the software
- Development takes store is and estimates costs
- Client prioritises stories
- Simple design - as simple as the current level of functionality allows. No extraneous complexity allowed
- When the code becomes too unwieldy its time for refactoring
- Design only extends to the next iterations new features
- Small Releases: XP development teams release tested, working code, very frequently
- Each iteration - 2 weeks - the client gets new code
- Client evaluates it and dictates the next delivery
- Consumer Test - The customer develops acceptance tests to see if software meets user stories
- Tests are automated and used frequently by the developers
- Pair Programming
- Test Driven Development
- Design Improvement - refactoring code whenever deficiencies are noticed = improving the design of the existing code
- Collective code ownership: immaterial who wrote the code; anyone can modify it at any time
- Whoever notices a problem, fixes it
- Continuous Integration: At all times the system compiles, runs and passes all tests
- Sustainable Pace: Same amount of work and effort in every iteration
- Overtime leads to burnout, mistakes and more burnouts
- Code standard - adopt some coding standard that is consistently adhered to
TDD
- Code standard - adopt some coding standard that is consistently adhered to
- Programming technique ensuring that code is thoroughly unit tested if a test fails then progress has been made: you know what to fix
- Clear measure of success when the test no longer fails
- TDD increases confidence that the system meets the requirements
- Side effect of TDD is you achieve 100% coverage test
- Every single line of code is tested
- Not guaranteed with traditional testing
- Does not replace traditional testing: just effective unit testing
- Side effective of TDD: the resulting tests are working examples for invoking the code -> provides a working spec for the code